Autologous Stem Cell Therapy
Illness, injury, and congenital defects can significantly hinder an individual’s quality of life, and sometimes they are beyond conventional medical treatments. Fortunately, over the last few decades, there has been groundbreaking progress in the field of regenerative medicine using autologous stem cells.
These are cells that are taken from the patient’s own adipose tissue and are used to prompt the body’s natural healing abilities to treat many different conditions. These stem cells have the remarkable potential to regenerate, repair, or replace damaged cells and tissues such as blood cells, muscle cells, and even brain cells.

Where Do Autologous Stem Cells Come From?
Autologous stem cells are currently sourced from two locations within the patient’s own body. The most widely known source is bone marrow, but over the past few decades, research has discovered that stem cells can also be harvested from fat cells taken from the abdomen, thigh, or other “fatty” locations on the body.
Stem Cell Regenerative Treatments
The results of stem cell therapy usage in clinical trials are proving to be incredibly hopeful in the field of regenerative medicine and even the fight against cancer. Doctors and researchers involved in stem cell therapy are witnessing firsthand the positive results of these treatments.
Stem cells have been discovered to be highly versatile and adaptable, so they can be used to treat many different issues. From repairing damaged brain tissue to fighting cancer and other conditions like autism, stroke, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, orthopedic and neurological problems, stem cell therapy holds great promise for improving the health and quality of life for the individuals affected by these challenging health conditions.
Where Do Autologous Stem Cells Come From?
Stem cells can be harvested from bone marrow or from fat cells to be used for stem cell therapy, and the origin chosen is dependent on the needs of the patient. Stem cells are special because when they are produced, they are like a blank canvas but eventually will become a specific type of cell depending on where in the body they are needed.
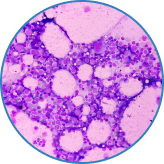
Bone marrow is a vital part of our body, and its job is to manufacture important cells like platelets and both red and white blood cells. Marrow is found inside the bones and can be described as a soft, squishy, and spongy tissue that is busy creating new cells.
Harvesting stem cells from bone marrow is a surgical procedure that is normally done under general anesthesia but usually does not require an overnight hospital stay. The extraction is typically done by inserting a needle into the iliac-crest hip bone and drawing it out with a syringe. Normally, incisions are not created to perform the extraction, and instead, several puncture locations are used.
After extracting the bone marrow from the target location, a special medical instrument called a centrifuge is used to spin it and separate out the desired cells. These cells are then injected into the areas that are targeted for stem cell treatment.

Subcutaneous fat is harvested from areas such as the stomach, thighs, buttocks, or hips using liposuction, or alternately, can be obtained through direct excision.
Once the fat is harvested, it is exposed to an enzyme that breaks it down and leaves only a concentration of stem cells. These stem cells are then mixed with platelet-rich plasma that was created by extracting blood from the patient and processing it in a centrifuge. This mixture is then injected into the location targeted for stem cell therapy.
Does Medical Insurance Cover Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy is still considered an experimental treatment and is not currently covered by health insurance. While many clinical trials have shown a great deal of success with using stem cells to treat various conditions, more research is needed to fully understand the benefits and risks involved.

